Home » Innovation & Technology » Beyond Plugs
Innovation & Technology
Beyond Plugs
stock.adobe.com / Koray
How Wireless Charging Technology is Revolutionizing Electric Public Transportation
Wireless charging technology charges electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches, without the need for cables or cords. It works by using electromagnetic fields to transfer power from a charging pad or station to the device that needs to be charged.
What is a Qi wireless device?
Literally meaning “vapor,” “air,” or “breath,” the word Qi is often translated as “vital energy,” “vital force,” “material energy,” or simply as “energy.” Pronounced “chee” Qi is the central underlying principle in Chinese traditional medicine and in Chinese martial arts. Qi is a wireless charging method from the Wireless Power Consortium. Introduced in 2009, Qi is based on “closely coupled” electromagnetic induction that requires the device to be aligned on top of the coil on the charging pad.
Wireless charging typically relies on two main components: a charging pad or station and a device with built-in wireless charging capabilities. The charging pad or station contains a coil that generates an electromagnetic field when it is connected to a power source. The device with built-in wireless charging capabilities also contains a coil that can receive the electromagnetic field and convert it back into electrical energy to charge the device’s battery.
Wireless Qi standard is version 1.2.4, was released by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) on September 23, 2021. This standard builds upon the previous versions and provides enhanced features such as improved communication between the charging pad and device, increased power transfer efficiency, and the ability to charge multiple devices simultaneously. Qi is the most widely adopted wireless charging standard and is used by a wide range of electronic devices, including smartphones, smartwatches, and wireless earbuds. Qi2, released in 2023 adds features and pushes the technology forward. The future of wireless Qi includes enhancements like Magnetic Power Profile which uses magnetic alignment to minimize energy loss.
Wireless charging has several advantages over traditional cable-based charging methods. It eliminates the need for multiple cords and chargers, which can be inconvenient and cluttered. It also allows for more flexibility in where devices can be charged, as they do not need to be connected directly to a power source. With emerging standards, wireless charging times are improving and becoming more efficient throughout the energy transfer process.
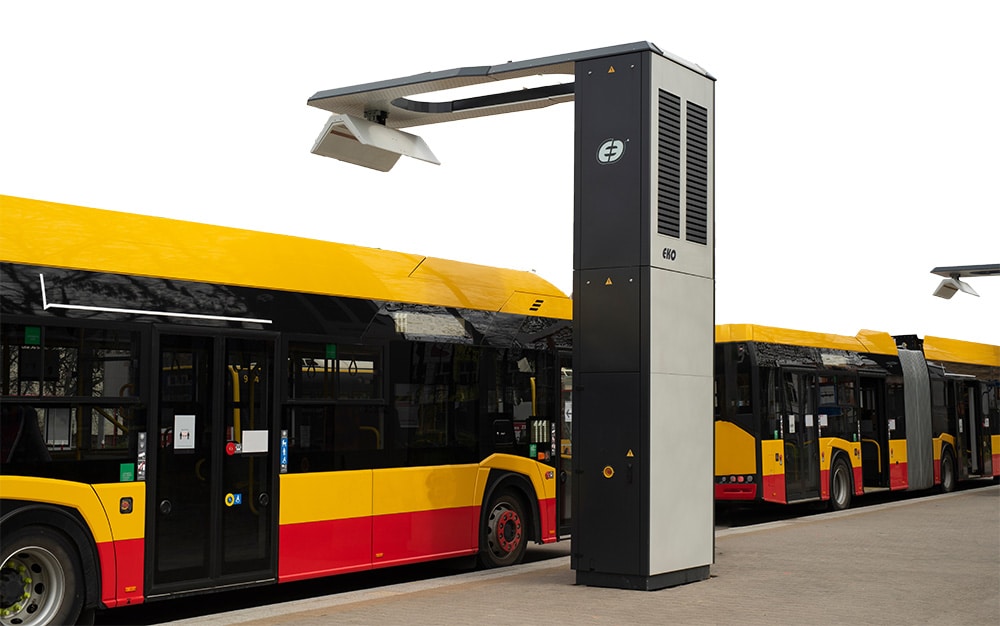
As of September 2021, there were several counties in the United States that had implemented wireless bus charging technology, including:
- King County, Washington: King County Metro, the public transportation agency for the Seattle metropolitan area, implemented wireless charging technology for its electric buses.
- Howard County, Maryland: Howard County Transit operated electric buses that use wireless charging technology.
- Monterey County, California: Monterey-Salinas Transit (MST) has implemented wireless charging technology for its electric buses.
- Solano County, California: Solano County Transit (SolTrans) operates electric buses that use wireless charging technology.
- Los Angeles County, California: Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LA Metro) has tested wireless charging technology for its electric buses.
What Improvements Can We Expect for Qi Standard Over the Next Five Years?
Overall, the advancements in Qi standards hold immense potential for revolutionizing electric bus operations:
- Reduced dependence on fossil fuels: Increased range and efficiency can lead to lower fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to cleaner air and environmental sustainability.
- Improved public transit experience: Faster charging times and shorter layovers can lead to more consistent and efficient bus schedules, enhancing passenger experience.
- Lower operational costs: Simplified infrastructure, faster turnaround times, and reduced maintenance requirements can translate to significant cost savings for transit agencies. ◆

stock.adobe.com / Michael

Joseph R. Madison II is Associate Director of Parking Operations for Kennesaw State University, and a member of IPMI’s Allyship & Equity Advisory Group.
-
Joseph R. Madison IIhttps://parking-mobility-magazine.org/author/joseph-r-madison-ii/January 8, 2024
References
- https://www.kuow.org/stories/hidden-wireless-technology-keeps-buses-moving-in-this-rural-washington-town
- https://cte.tv/project/cmrt-inductive-electric-bus-deployment/
- https://www.sfchronicle.com/travel/article/State-s-first-wireless-electric-bus-rolls-on-14414606.php
- https://bus-news.com/us-soltrans-deploys-electric-highway-bus-and-wireless-charger/
- https://atlaspolicy.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Deploying-Charging-Infrastructure-for-Electric-Transit-Buses-1.pdf