Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Mobility
Smart Parking & Intelligent Transportation Systems
IN 2015, the United Nations approved 17 Sustainable Development Goals to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all. Goal 11 pertains to Sustainable Cities and Communities and is about making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. New technologies are a key element to accomplish these goals.
The idea of “smart cities” will continue to undergo structural changes, along with the implementation of laws that will allow the citizen’s quality of life and the environment to be at the forefront of all political and technological choices. How can cities meet their environmental goals? What effect does technology have on public administrations’ goals for city planning and modeling?
What do we know about smart cities? Smart cities mix planning, analysis, and technology to make decisions more effectively and raise the standard of living for their citizens. This involves having access to technical solutions that enable quick and effective need responses in terms of safety, weather, health, environmental quality, and connection. Artificial intelligence (AI) has a great deal of promise to enhance urban life.
One of the essential components of the smart city idea is mobility. Real-time management and traffic modeling are top priorities when implementing new technologies for intelligent and sustainable mobility. This makes AI-based solutions the perfect ally for overcoming the significant issues faced by big cities.
Table of Contents
Technology Evolution: Deep Learning, Machine Learning, and AI
The idea of AI being used in our daily lives, including voice assistants, mobile devices, and domestic appliances, is not new. Making robots capable of acting like humans have come to be associated with artificial intelligence. The so-called “fourth industrial revolution” is ushered in by AI, but how did we get here? How is it feasible to create technical innovations that behave and learn like people?
A turning point was reached in the 1950s when mathematical and physical scientists started to explore the concept of AI and look into its full potential. The physicist and mathematician Alan Turing suggested a test in 1950 to determine whether a machine could replicate human behavior. Additionally, John McCarthy, a computer scientist, first used the term “artificial intelligence” in 1956 at the Dartmouth conference.
Although they are all closely connected to machine intelligence, the concepts of AI, machine learning, and deep learning have some differences.
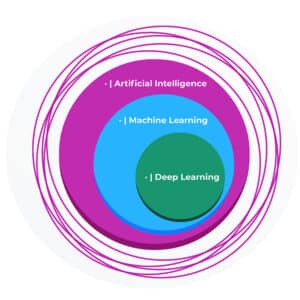
- Artificial Intelligence: Technique that allows a machine to imitate human behavior.
- Machine Learning: Technique to achieve AI through algorithms trained with data.
- Deep Learning: Type of machine learning inspired by the structure of the human brain.
AI can gather and organize huge amounts of data to make judgments and predictions that are beyond the capacity of humans to understand manually. Because of its potential, it can be more effective while reducing risk and error of all kinds. In traffic applications, artificial vision is utilized because proper management of digitized traffic necessitates the capture and management of vast volumes of data that a human cannot manage. This artificial vision allows traffic camera images to be analyzed and transformed into pertinent information, but its primary technological constraint is the trade-off between accuracy and processing speed; the more accurate the analysis is desired, the longer it will take to complete.
Due to its analytical ability, which enables forecasting and automating specific behaviors in specific situations, AI emerges as the primary force driving change in smart cities when it comes to mobility. These new technologies are becoming more and more prevalent in our daily lives, improving our quality of life and addressing issues that may arise every day.
Technology based on AI can help smart cities fulfill their ecological and coexistence commitments. Unquestionably a significant challenge.
Smart Parking: The Power of Apps.
The terms “parking on-street” and “parking off-street” were once connected to two distinct markets in which distinct actors (customers and suppliers) engaged. A change happened when the on-street and off-street parking markets started to converge because of the introduction of parking reservation and payment apps, which technologically changed the parking industry.
Vehicle identification via the license plate (LPR) has become a crucial component in ensuring the reservation and payment procedures in parking lots. As soon as users of on-street and off-street car parks start using mobile apps, the license plate becomes a reliable method of identifying the vehicle. Reading the number plates is the automatic method of clearly identifying the car. As a result, the technology utilized for license plate reading and identification must match the standards for LPR systems in terms of accuracy rate, usefulness, and versatility. Using deep learning algorithms to analyze video for LPR enables a greater accuracy rate and increases the advantages of intelligent on-street and off-street parking management.
The most sought-after parking management solutions now include ticketless and barrierless systems, as well as ones that enhance the seamless user experience, thanks to the development of smart Automated License Plate Readers (ALPR) systems based on artificial intelligence.

The highest feasible accuracy rate and a guarantee of a 99.99% quality of service are priorities when converting a system to barrierless or ticketless operation. These goals allow the system to operate continuously. To accomplish this goal, various tactics are used to ensure both goals, including the following crucial components:
Video Analysis Technology
Deep learning networks, dated pattern-matching methods, and traditional neural network algorithms can all be employed as the foundation for video analysis. Deep learning, the newest and most potent of the three machine learning alternatives, makes a difference in terms of performance, accuracy, and the variety of potential applications.
Placement of Cameras
The placement of cameras at access points directly affects the LPR system’s accuracy rate. It is crucial to have a system that can adapt to diverse types of roadways (complex lanes, lane widths, and diversity of vehicle types).
Operation Mode (Trigger vs. Free-Flow)
Depending on whether an entrance is traditional, ticketless, or barrierless, there may be many operational modes in parking systems. The LPR system must therefore be capable of adapting to the various forms of access by using license plate reading and analysis techniques with an external trigger or in free-flow mode.
Use of Multiple Cameras on the Lane
The LPR accuracy rate can be improved and the 24/7 operation is ensured by using multiple cameras in a lane. The synchronization of the results from the different cameras is essential for success to deliver the highest performance and prevent confusion between readings from various vehicles. It is truly important to have the possibility to set up the synchronization in trigger-equipped or free-flow lanes, as well as barrierless ones.
How can parking management in projects including ticketless or barrier-free parking be made more effective? Given that deep learning has been demonstrated to be the most effective machine learning technique for video analysis, LPR systems based on these algorithms are advised. A system that enables working with both black and white photos with IR illumination and color images with white light, as needed in each location, is also essential. Additionally, it is advised that you permit the use of numerous cameras on the same lane to synchronize them, either by an external trigger or in free-flow mode, without a trigger, in order to ensure round-the-clock operation.
This technical combination ensures optimum efficiency and profitability in parking systems and delivers unmistakable results in terms of hit rate, reaching over 99%.
Smart Mobility: Sustainability Rules!
Markets like parking and intelligent transportation systems (ITS) are becoming more interconnected because of the development of video analysis tools based on AI technology. A new idea like “smart mobility,” which integrates parking and ITS solutions with the goal of making cities inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable, will emerge as a result of this union.
What effects does emerging technology have on urban areas? The development of numerous intelligent applications for the management of low CO2 emission zones, for the management of incidents and traffic violations in real-time, for the early detection of traffic congestion situations, and for the implementation of smart traffic lights is made possible by video analysis solutions based on deep learning.

The following are some advantageous uses of artificial intelligence in mobility management:
- Traffic gauging up and classification (cars, bicycles, motorbikes, scooters, buses, vans, lorries, and pedestrians).
- Identification of the vehicle type, make, and color.
- Automatic License Plate Recognition (ALPR).
- Vehicle queue management.
- Curbside management through the detection of vacant or occupied places.
The main competitive advantage of intelligence-based video analysis systems is the generation of pertinent information in real-time that enables those in charge of traffic management to plan effectively and react swiftly to emergencies. These systems are capable of detecting and classifying vehicles in real time, even detecting violations and incidents instantly. Assuming an optimal instrument for the implementation of smart cities, all of this creates useful information for the modification of traffic based on reality in order to reduce traffic jams, pollution, accidents, and infractions.
Technology makes it happen.
The fourth industrial revolution has been created as a result of the development of digital technologies, which have also transformed the globe, the economy, and industry. The industry has benefited from these advancements, but they have also helped us live better daily lives. The task at hand is clear: rely on technical innovation to enable the adoption of a variety of mobility applications in smart parking lots and smart cities. By relying on effective, foresightful, and environmentally friendly technology, this will enable public administrations and businesses in the parking sector to innovate and update their management practices. Are you prepared for change? ◆
-
This author does not have any more posts.


A Glimpse of the Future
From the Editor Melissa Rysak, editorrysak@parking-mobility.orgAt the IPMI Leadership Summit

Exploring the Power of Smart Parking
An Ally for a Greener Tomorrow